Back
Cardiac: Other
Association Between Periodontal Disease and Heart Failure: A Meta-Analysis

Purpose: Multiple chronic inflammations, infections, and autoimmune diseases are associated with higher risks of cardiovascular events. Periodontal disease is one of the most prevalent systemic inflammatory diseases worldwide. However, the association between periodontal disease and heart failure is not well-described. We, therefore, conducted a meta-analysis to investigate the association between periodontal disease and heart failure.
Material and Methods: We independently searched the databases of MEDLINE and EMBASE from the inception to December 15, 2022. We included cohort studies that evaluate the association between periodontal disease and heart failure risk. Data from each study were combined using the random-effects model to calculate pooled odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (CI).
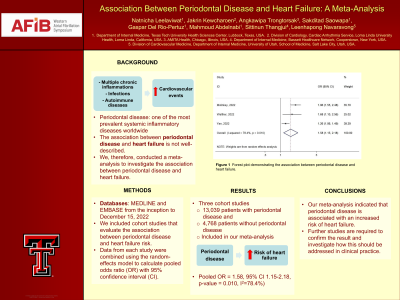
Results: A total of three cohort studies involving 13,039 patients with periodontal disease and 4,768 patients without periodontal disease were included in our meta-analysis. We found that patients with periodontal disease have a significantly higher risk of heart failure with the pooled OR of 1.58 (95% CI 1.15-2.18; p=0.005, I2=78.4%).
Conclusions: Our meta-analysis indicated that periodontal disease is associated with an increased risk of heart failure. Further studies are required to confirm the result and investigate how this should be addressed in clinical practice.
Material and Methods: We independently searched the databases of MEDLINE and EMBASE from the inception to December 15, 2022. We included cohort studies that evaluate the association between periodontal disease and heart failure risk. Data from each study were combined using the random-effects model to calculate pooled odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (CI).
Results: A total of three cohort studies involving 13,039 patients with periodontal disease and 4,768 patients without periodontal disease were included in our meta-analysis. We found that patients with periodontal disease have a significantly higher risk of heart failure with the pooled OR of 1.58 (95% CI 1.15-2.18; p=0.005, I2=78.4%).
Conclusions: Our meta-analysis indicated that periodontal disease is associated with an increased risk of heart failure. Further studies are required to confirm the result and investigate how this should be addressed in clinical practice.
